Heres a step by step guide to adding TLS encryption to your Postgres database in Dokploy. This will ensure secure connections between the DB and your app. Here’s how I managed it using volumes in Dokploy:


1. Generate a Certificate Authority (CA)
openssl genrsa -out rootCA.key 2048
openssl req -x509 -new -nodes -key rootCA.key -sha256 -days 3650 -out rootCA.crt -subj "/CN=MyLocalCA"2. Generate a Server Certificate Signed by Your CA
Create a config file server-cert.conf with your hostnames/IPs.
I added my staging domain “st.domain.com” and the staging api “st-api.domain.com” for my staging environment.
[req]
default_bits = 2048
prompt = no
default_md = sha256
distinguished_name = dn
req_extensions = req_ext
[dn]
CN = st-api.yourdomain.net
[req_ext]
subjectAltName = @alt_names
[alt_names]
DNS.1 = st-api.yourdomain.net
DNS.2 = st.yourdomain.net
DNS.3 = localhost
IP.1 = 127.0.0.1
IP.2 = 192.168.200.149
[req]
default_bits = 2048
prompt = no
default_md = sha256
distinguished_name = dn
req_extensions = req_ext
[dn]
CN = st-api.yourdomain.net
[req_ext]
subjectAltName = @alt_names
[alt_names]
DNS.1 = st-api.yourdomain.net
DNS.2 = st.yourdomain.net
DNS.3 = localhost
IP.1 = 127.0.0.1
IP.2 = 192.168.100.123
The last line should be the ip to your server.Then run:
openssl genrsa -out server.key 2048
openssl req -new -key server.key -out server.csr -config server-cert.conf
openssl x509 -req -in server.csr -CA rootCA.crt -CAkey rootCA.key -CAcreateserial -out server.crt -days 365 -sha256 -extfile server-cert.conf -extensions req_extThis should get you a server.crt file and a server.key file created.
3. Prepare the Docker Volume
Start a temporary container to access the Dokploy volume:
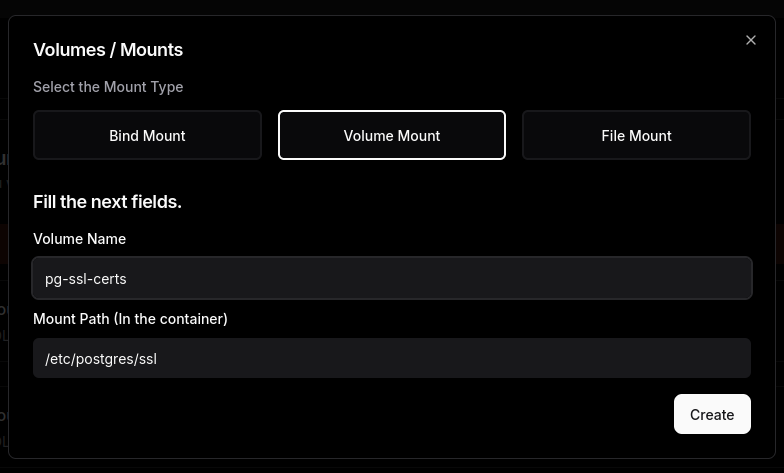
Go to your Postgress application in Docker (Projects> Postgress > Advanced tab)
Scroll down to volumes and click “Add Volume”.
Select “Volume” from the tab and give it a name. For bind path use “/etc/postgres/ssl”.
Go back to the General tab and deploy it.
Now that its running were going to SSH into the server in a terminal and type:
docker run --rm -it --name my-busybox -v pg-ssl-certs:/data busybox sh
busyboxis a tiny, lightweight Linux utility image commonly used in Docker for troubleshooting, scripting, or quick file operations.
Leave that running and in another terminal, ssh again into the server and were going to use a docker copy the server crt and key into the container we just opened with busybox. The previous command named the container “my-busybox” so we can refer to it in the following line but you can name it anything. Its temporary.
docker cp server.crt my-busybox:/data/server.crt
docker cp server.key my-busybox:/data/server.keyBack inside the busybox shell, set permissions:
chmod 600 /data/server.keySet the Postgres Command in Dokploy
In the “Command” field:
docker-entrypoint.sh postgres -c ssl=on -c ssl_cert_file=/etc/postgres/ssl/server.crt -c ssl_key_file=/etc/postgres/ssl/server.key6. Redeploy Postgres
Redeploy your Postgres app in Dokploy.
7. Test SSL
Back in the shell to your server connect with psql:
psql "host=YOUR_DB_HOST user=YOURUSER dbname=YOURDB sslmode=require"in the following psql prompt:
SHOW ssl;You now have a secure, TLS-enabled Postgres instance running in Dokploy.